
Iron-Based Metal Organic Framework Shows Stability for Energy Storage Explore breakthroughs in supercapacitor technology with Fe-Tp MOFs—listen now! Smartphones and electric cars both need energy sources that charge quickly and last long—the kind of power supercapacitors deliver, unlike traditional batteries. But the use of acids in such devices can hinder the advancement of energy storage materials development, a limitation that researchers at Khalifa University have addressed by developing a new iron-based conjugated metal–organic framework (Fe-Tp MOF). The research findings have been protected by a US patent application. The research was published in a paper titled ‘Iron salicylaldehydate…
Read more
New approach turns a greenhouse gas problem into a sustainable energy solution As the world grapples with the escalating impacts of climate change, finding effective ways to reduce carbon dioxide emissions has become more urgent than ever. Traditional methods of CO2 capture, though effective, often face challenges in terms of scale, energy use and expense. Researchers have now developed an innovative method that could provide a seamless process to capture CO2 and convert it into a useful product: methane. This study aspires to revolutionize studies relevant to Power-to-Methane application as well as deploy smart and affordable ways to…
Read more
Dr. Sharmarke Mohamed to Lead Two International Crystal Engineering Conferences in 2026 and 2028 Khalifa University’s Dr. Sharmarke Mohamed, Associate Professor of Chemistry, Head of the Chemical Crystallography Laboratory (CCL) and Theme Leader in the Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS), has been elected by the solid-state chemistry community to co-chair the 2028 Gordon Research Conference (GRC) in Crystal Engineering. The election of Dr. Mohamed took place during the business meeting of the 2024 GRC in Crystal Engineering, held from 23-28 June 2024 in Newry Maine, US. It marks a four-year commitment for Dr. Mohamed to help organize…
Read more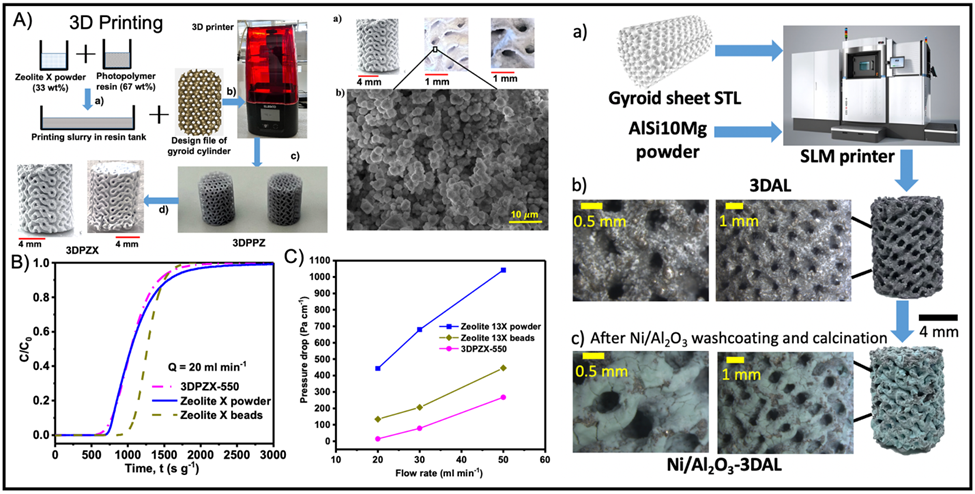
Catalysis and 3D Printing Fields Converge to Transform Carbon Dioxide Decarbonization Researchers from Khalifa University's Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS) and Advanced Digital & Additive Manufacturing (ADAM) Group are merging the fields of catalysis and 3D printing to develop groundbreaking technologies for capturing and converting carbon dioxide (CO2), a critical step in addressing the global challenge of decarbonization. This is part of the SynERGON joint initiative in CeCaS, which aims to break the silos and create more areas of collaboration among traditional and contemporary fields of research towards creation of innovative solutions. Published in Separation and Purification…
Read more
Dr. Ahsan Ul Haq Qurashi Will Oversee Manuscripts Related to Electrocatalysis and Nanotechnology for Clean Energy Applications Khalifa University faculty Dr. Ahsan Ul Haq Qurashi, Deputy Director, Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCAS), and Associate Professor, Chemistry has been appointed to the editorial board of Springer Nature’s Communications Engineering to oversee manuscripts related to electrocatalysis and nanotechnology for clean energy applications. Communications Engineering, a journal that supports Springer Nature’s effort to advance progress towards the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) publishes research papers that represent developments for specialized areas. Dr. Qurashi is already the editorial…
Read more
An innovative electrochemical process unlocks the potential of mining wastewater by recovering valuable metal ions and transforming them into valuable end products for a greener future. A team of researchers from Khalifa University’s Center for Membranes & Advanced Water Technology (CMAT) and Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) has developed a sustainable electrochemical process to recover metal ions in wastewater, turning them into valuable end products for energy conversion and storage applications. Dr. Bharath Govindan, Research Scientist, Abdul Hai, Research Associate, Dr. Rambabu Krishnamoorthy, Postdoctoral Fellow, Dr. Mohammad Abu Haija, Associate Professor, and Prof. Fawzi Banat, Chair of the Chemical…
Read more
The scope of this event was to bring together scientists, engineers, and industrial partners across the globe to discuss the current advances, local and global challenges, and sustainable solutions in the fields of catalysis and separation towards achieving net zero carbon emissions and sustainability. This particular workshop focused on: Greener catalytic and separation processes/ technologies Green and sustainable materials development Net zero-carbon emissions Circular economy Life-cycle analysis The invited speakers from the Abu Dhabi Ports Academy (Dr. Yaser AlWahedi), BASF Middle East (Mrs. Elena Petriaeva and Mr. Manish Mehta), and ADNOC (Mrs. Hanin Radman) exchanged their knowledge with…
Read more
Workshop Agenda Registration Link
Read more
Sustainable fuels are within reach but processes need to be optimized for low-cost industrial scale production. Converting hydrogen and carbon dioxide into methanol for sustainable fuel is one route, but the reaction pathway needs elucidating and catalysts optimizing. A team of researchers from Khalifa University has developed a model to do just that. Transforming carbon dioxide emissions into value-added products like methanol for fuel is essential for the development of a circular economy and reducing anthropogenic impact on the atmosphere. But the process of developing these products can introduce side reactions that can significantly influence efficiency and the quality…
Read more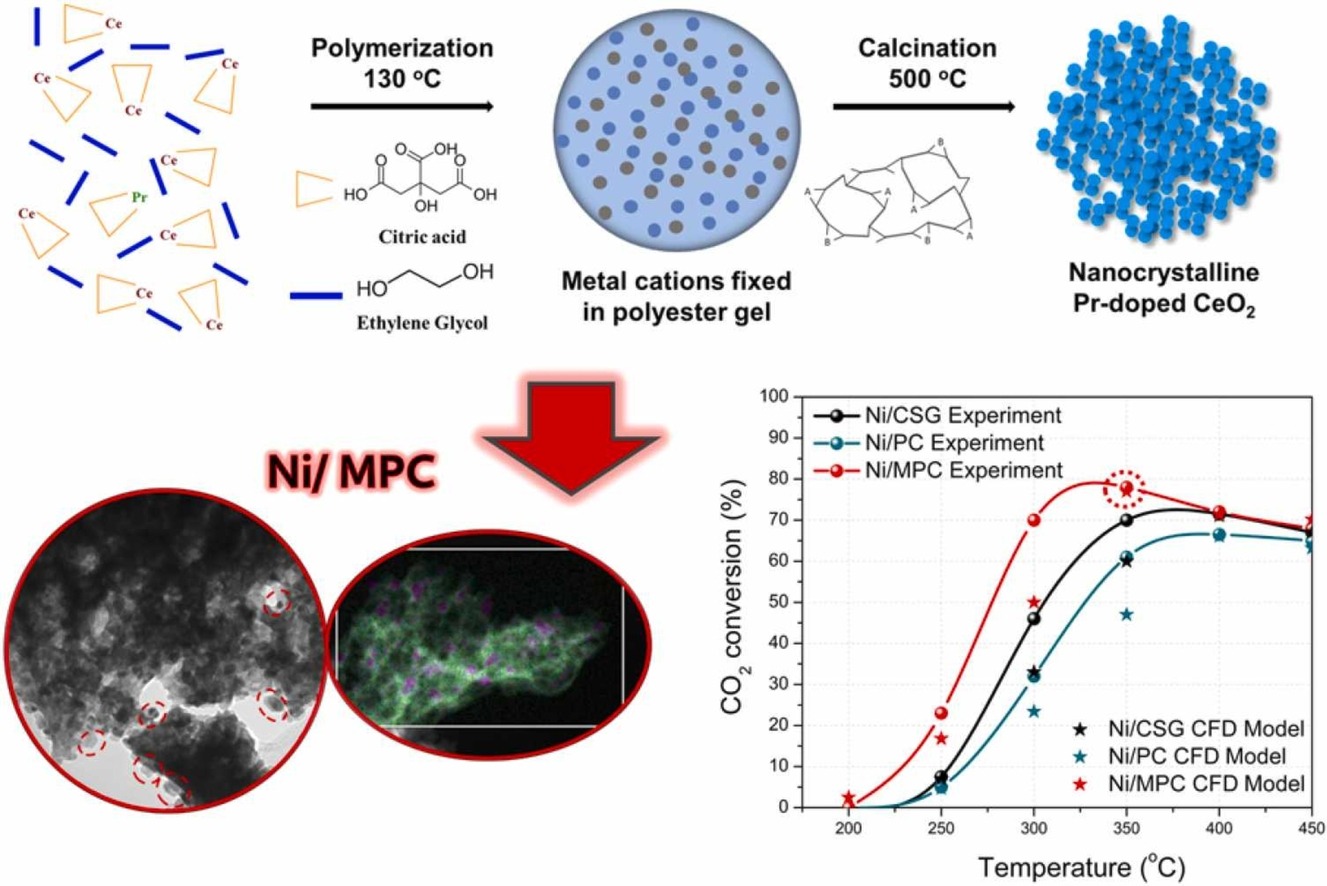
A simple and straightforward method can be used to develop catalysts for the chemical process that turns carbon dioxide emissions into high-energy-density fuels. Nickel nanoparticles and cerium(IV) oxide combine to make a catalyst more than 50 percent more effective than already existing catalysts. A team of researchers including Dr. Aasif Dabbawala, Prof. Kyriaki Polychronpoulou and Aseel Hussein from Khalifa University’s Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) has developed a new catalyst for transforming carbon dioxide emissions into fuels that could be used for space travel and Mars exploration missions. The CeCaS team collaborated with researchers from University College…
Read more
Researchers at Khalifa University’s Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) have been granted two patents for their work on the effect of magnetic fields on separating mixtures and detecting gases. Gas separation is a process used across myriad disciplines and industries, with use cases ranging from purifying natural gas and removing carbon dioxide to producing oxygen for medical use and nitrogen for chemical feedstocks. There are various ways of separating gases in a mixture, including absorption, distillation, and membrane separation. Dr. Georgios Karanikolos, Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering, developed a new method for gas separation, using magnetic…
Read more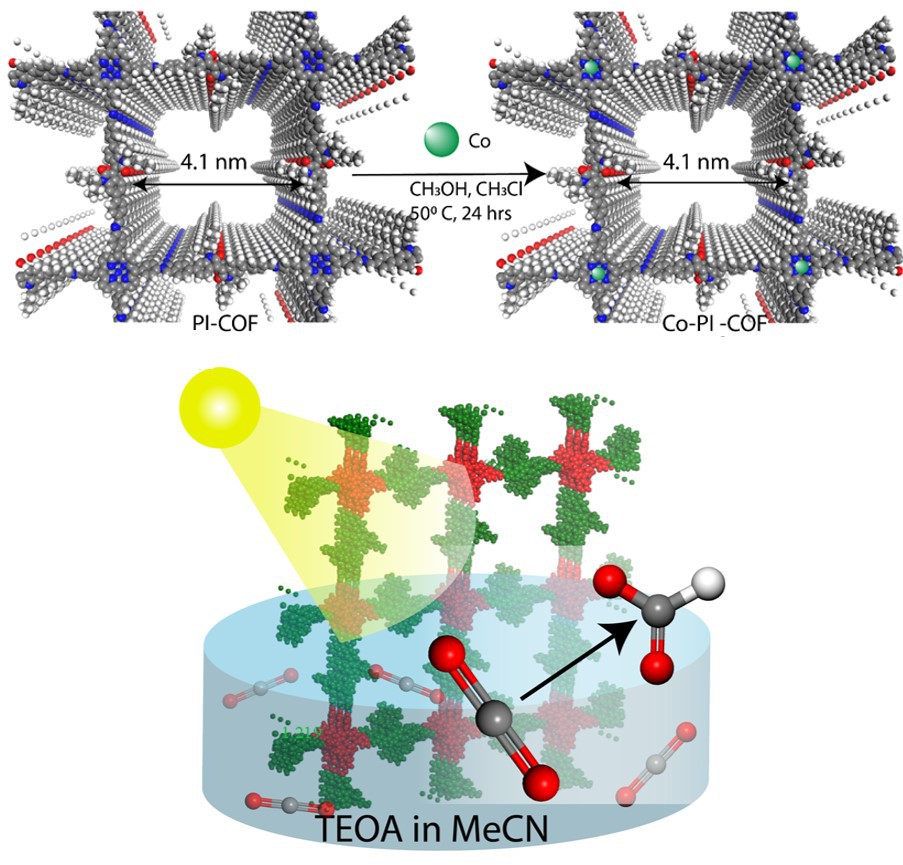
International research team including Khalifa University paves way towards the design of new simple and efficient photocatalysts made from covalent organic frameworks (COFs) to reduce captured CO2 into useful products As the world continues to pump carbon into the atmosphere, it is increasingly important to not only reduce emissions but also find ways to capture and use carbon dioxide. Carbon capture and storage technologies are noble approaches, but don’t tend to make much money. Instead, attention turns to economically viable and valuable approaches to turn carbon dioxide into something useful. Dr. Dinesh Shetty, Assistant Professor of Chemistry,…
Read more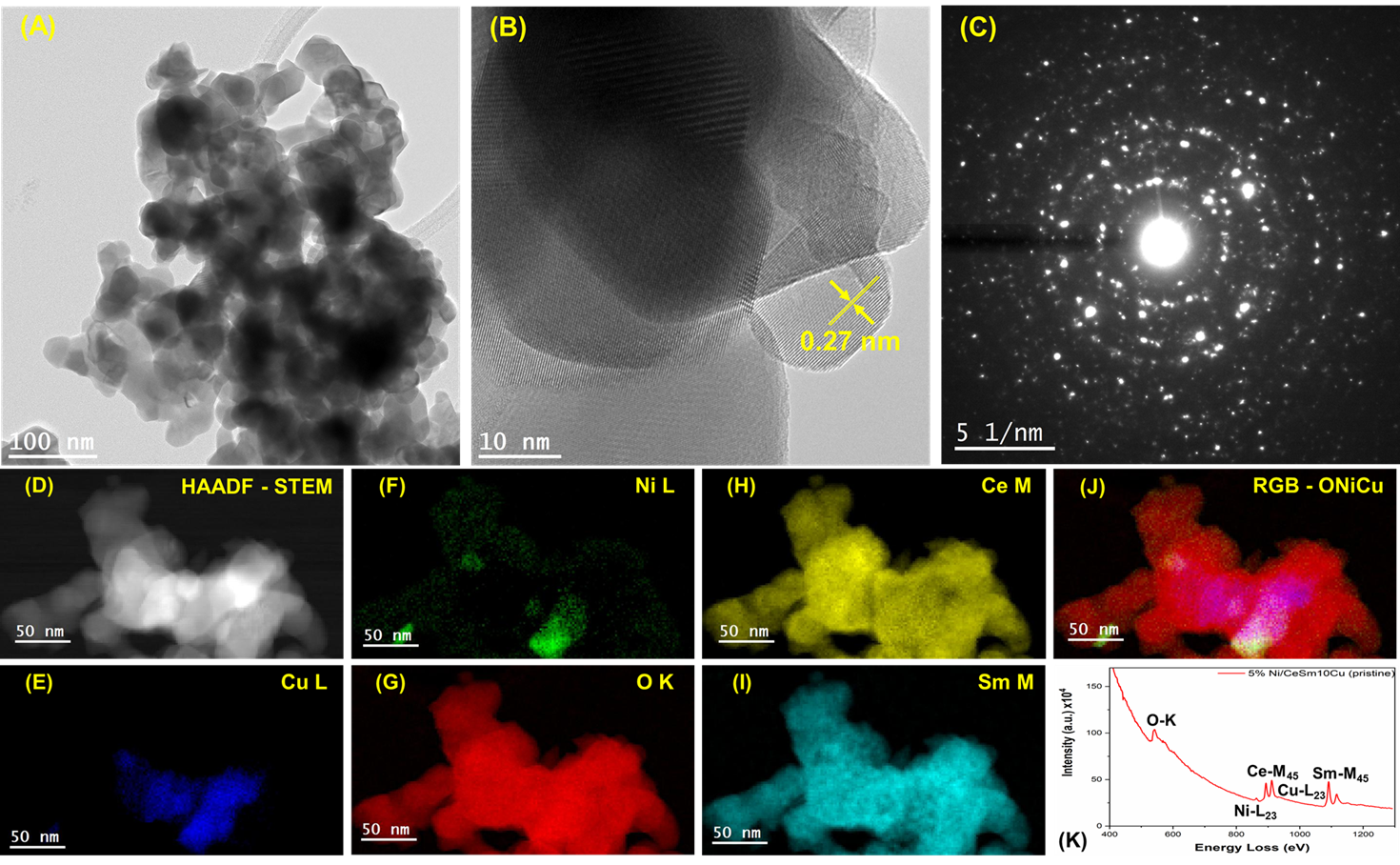
Dr. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Director of the Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) at Khalifa University, and her research group have recently authored a paper on dry reforming of methane that was published in the prestigious journal Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, with an impact factor of 19.5 (Elsevier, Q1). The KU research group was led by Dr. Polychronopoulou and included Aseel Hussien, PhD Student, Dr. Aasif Dabbawala, Postdoctoral Fellow and co-advisors Dr. Maryam Khaleel, Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering, and Dr. Dalaver Anjum, Assistant Professor of Physics. This work was the result of a fruitful…
Read more
Dr. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Director of the Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) at Khalifa University, and her research group successfully participated in the Materials Research Society (MRS) Fall 2021 Meeting in Boston, Massachusetts, USA, which was held from 29 November till 2 December 2021. The MRS conference is an international platform for materials research that brings together researchers from fields of chemistry, biology, physics, and engineering. Among the eminent keynote speakers at the conference was Sir Fraser Stoddart, 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. The work of two KU PhD students from CeCAS was…
Read more
Understanding the role of the surfaces and internal structure of the nanocrystal will help researchers develop more effective and efficient catalysts for many important catalytic processes. A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without being consumed in the process. They typically speed up the reaction by reducing the energy needed to activate the reaction or by changing the mechanism by which the reaction occurs. Catalysis is one of the pillars of the chemical industry, so developing effective and efficient catalysts for a wide range of uses is crucial.…
Read more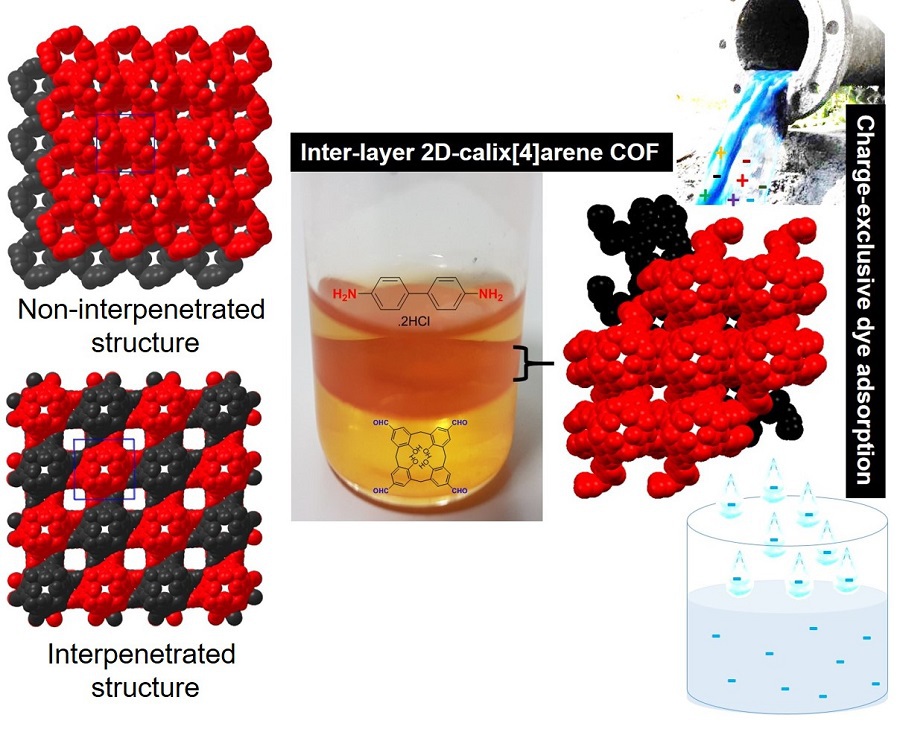
KU Researcher worked with NYUAD to create the first woven calixarene-based covalent organic framework (COF) with plenty of tunable pores for adsorption applications Read Arabic story here. Synthetic dyes are common ingredients in the textile industry, but because of their general use, they often find their way into waterbodies from industrial wastewater, where they pollute the water and threaten water security. Removing these polluting dyes can be achieved through adsorption, where the dyes are collected in the pores of highly porous materials that scoop the pollutants from water and trap them in the pores. Dr. Dinesh…
Read more
Removing paraquat from agricultural wastewater is crucial to protecting the environment and human health but conventional materials to do so are slow-acting and not reusable. Dr. Dinesh Shetty at KU has developed a novel polymer to adsorb paraquat much more efficiently. Read Arabic story here: http://www.researchku.com/news-7-extended.php?id=7 Water quality is influenced by many natural factors but the greatest threat comes from human activity. Mining, urban development, and agriculture are among the biggest culprits, introducing pollutants into the waterways from various processes. If they enter drinking water sources, they can pose a significant threat to human health. Paraquat is a…
Read more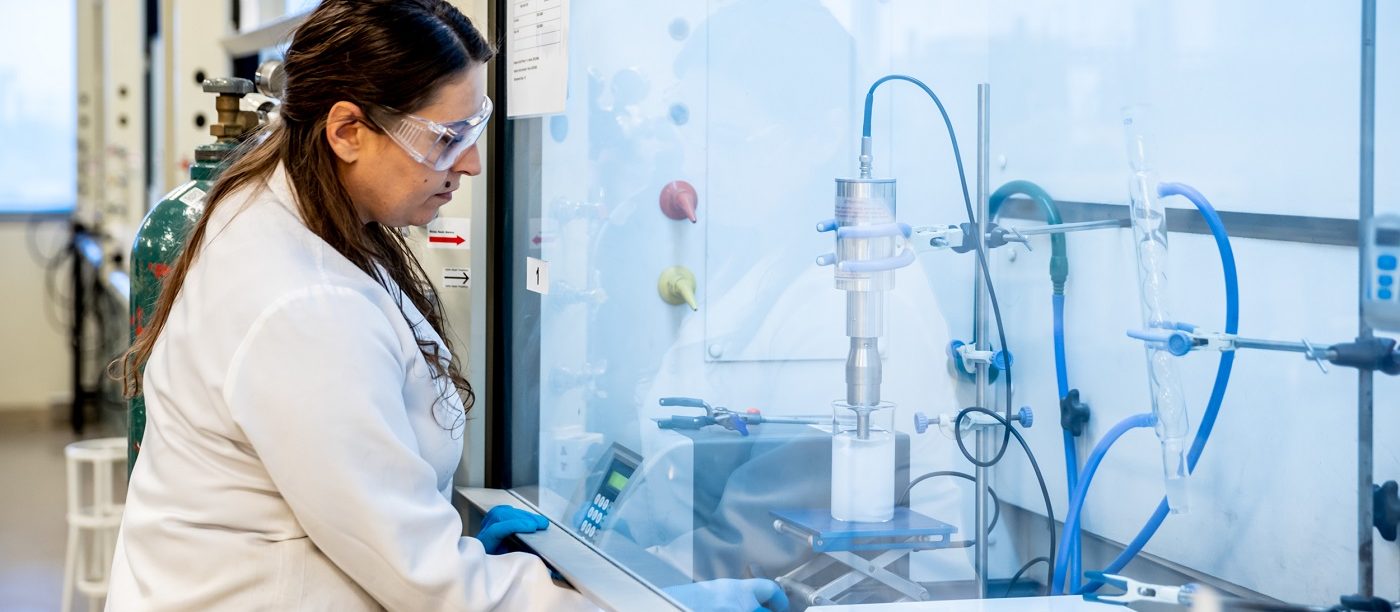
Researchers from Khalifa University have developed a simple method to produce catalysts more efficiently and precisely, which could help accelerate the development of super effective catalysts for numerous industries. A team of researchers led by Dr. Yasser Al Wahedi, Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering at Khalifa University and a member of the Center for Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS), and Dr. Georgia Basina, Post-Doctoral Fellow in the same department, have developed a new way of making catalysts that is more precise and effective. This simple and effective method involves embedding nanoparticles in a material dotted with ultra-small pores, known…
Read more
Sara Alkhoori is a full-time MSc student in mechanical engineering under the supervision of Assoc. Prof. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou. Her MSc thesis is focused on improving metal oxide catalysts for biogas dry reforming reaction by coupling mechanochemical synthesis with enhanced microwave chemistry. Earlier this June, she was invited to visit university of Surrey in England during the period 15th to 30th of June for an organized study program on surface analysis training using the state-of-art x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). This technique is used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material by identifying the elements on the surface and quantifying their…
Read more
Ayesha Abdulla Alkhoori is a PhD student in Prof. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou’s group. She works as a full-time student under the Center of Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS). Alkhoori is majoring in Materials Science and Engineering. Her PhD thesis is focused on developing materials for hydrocarbon transformations coupling catalysis and separation. Ayesha gave two oral presentations in the 3rd ANQUE-ICCE International Congress of Chemical Engineering, which took place in Santander (Spain) from June 19th to 21st, 2019. The first talk titled “Improving Metal Oxide Catalysts for Biogas Dry Reforming: Coupling of Mechanochemical Modification with Enhanced Microwave Chemistry”. This research investigated the microstructure…
Read more
Mrs. Margarida Ferreira, was a visiting student of the Center of Catalysis and Separations (CeCaS) supporting the modeling work we are doing in CeCaS under Theme 3 ‘Multi-scale Modeling’, and embracing the existing collaboration between the research group she belongs to in Lisbon (Portugal) and our KU research group. Mrs. Margarita Ferreira, presented the joined work in the International Conference on Properties and Phase Equilibria for Product and Process Design, PPEPPD, held in Vancouver, CANADA, on May 12-16, 2019. [Photo: Mrs. Ferreira explaining her poster to Prof. Joan Brennecke, the editor in chief of the Journal of Chemical and Engineering…
Read more
Two PhD students under the supervision of Dr. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Director of the KU Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS), presented papers at the Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit & Exhibition (SIPS), which took place in Cyprus in October, demonstrating KU’s strong research capabilities in the field of catalysis. Ayesha Alkhoori presented a paper titled “H2 Production from Glycerol Steam Reforming.” Her paper describes how she has developed an improved catalyst capable of producing high yields of hydrogen by steam reforming glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel production, at a low temperature. A recent spike in…
Read more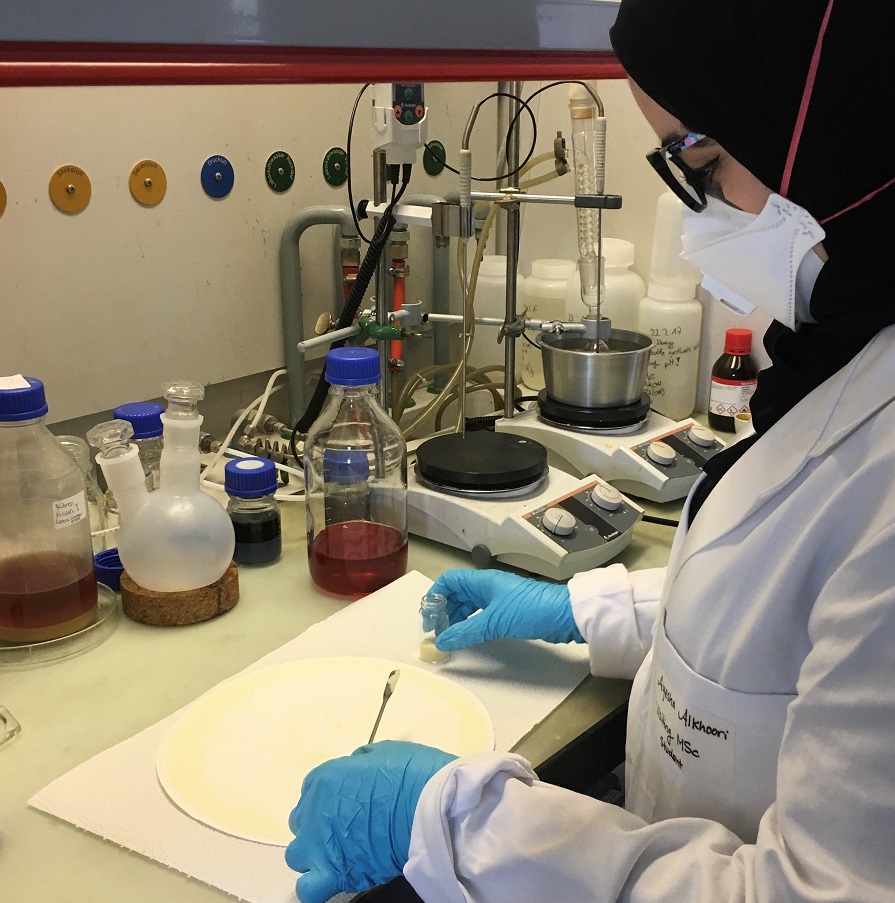
Two PhD students under the supervision of Dr. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Director of the KU Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS), presented papers at the Sustainable Industrial Processing Summit & Exhibition (SIPS), which took place in Cyprus in October, demonstrating KU’s strong research capabilities in the field of catalysis. Ayesha Alkhoori presented a paper titled “H2 Production from Glycerol Steam Reforming.” Her paper describes how she has developed an improved catalyst capable of producing high yields of hydrogen by steam reforming glycerol, a by-product of biodiesel production, at a low temperature. A recent spike in…
Read more
A team of researchers from Khalifa University has discovered an easy, low-cost and sustainable way to make catalysts that can split oxygen molecules from water, and in turn, produce hydrogen for energy storage and clean fuel applications. The new catalyst, which is made of electrodeposited metallic elements cerium, nickel and iron, can split oxygen from water (called the Oxygen Evolution Reaction, or OER) at a rate that is two times more efficient than conventional catalysts, which are primarily made from noble metal oxides. The collaborative team includes KU Post-Doctoral Researcher Dr. Ranjith Bose, KU Professor of Chemical Engineering Dr. Akram…
Read more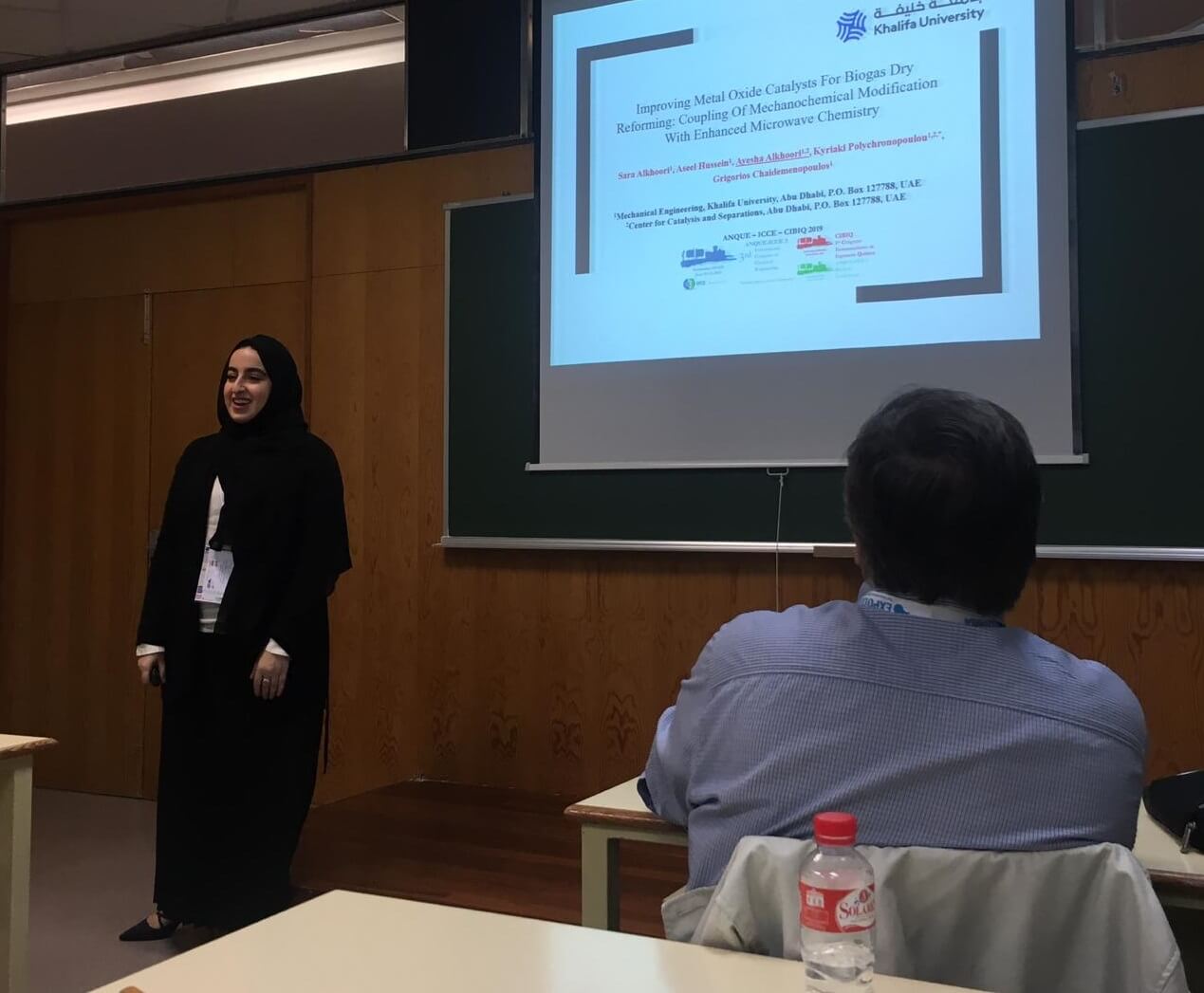
First PhD student from KU’s Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS) delivers two talks at International Conference in Spain on her pioneering catalysis research KU PhD student Ayesha AlKhoori delivered two talks on her pioneering research in the field of catalysis and separation at the 3rd ANQUE-ICCE International Congress of Chemical Engineering, held in June in Santander, Spain. Alkhoori is the first PhD student to study under the Petroleum Institute’s Center for Catalysis and Separation (CeCaS) at Khalifa University. Working under Dr. Kyriaki Polychronopoulou, Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering and Director of CeCaS, Alkhoori is helping to advance catalysis…
Read more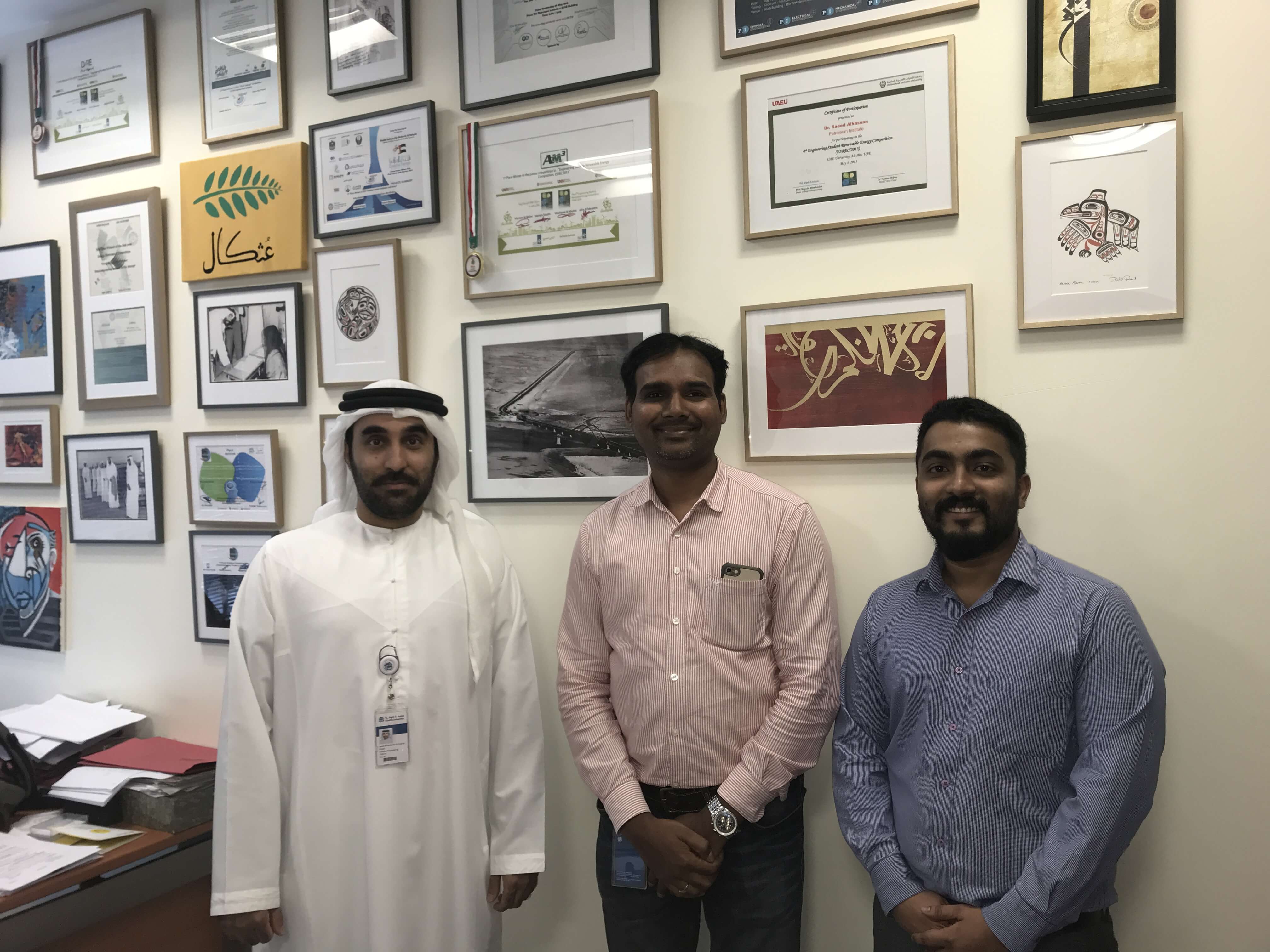
Paper by Dr. Saeed M. Alhassan, Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering, and researchers Dr. Sunil P. Lonkar and Dr. Vishnu V. Pillai, announced as one of Scientific Report’s top 100 papers in Chemistry A paper authored by Khalifa University researchers that explains a new method for developing high-efficient photocatalysts – materials that absorb sunlight to cause a chemical reaction – has been named one of 2019’s top 100 most important papers in the field of Chemistry in the renowned journal Scientific Reports. The paper, titled “Facile and scalable production of heterostructured ZnS-ZnO/Graphene nano-photocatalysts for environmental remediation,” identified an affordable, scalable,…
Read more