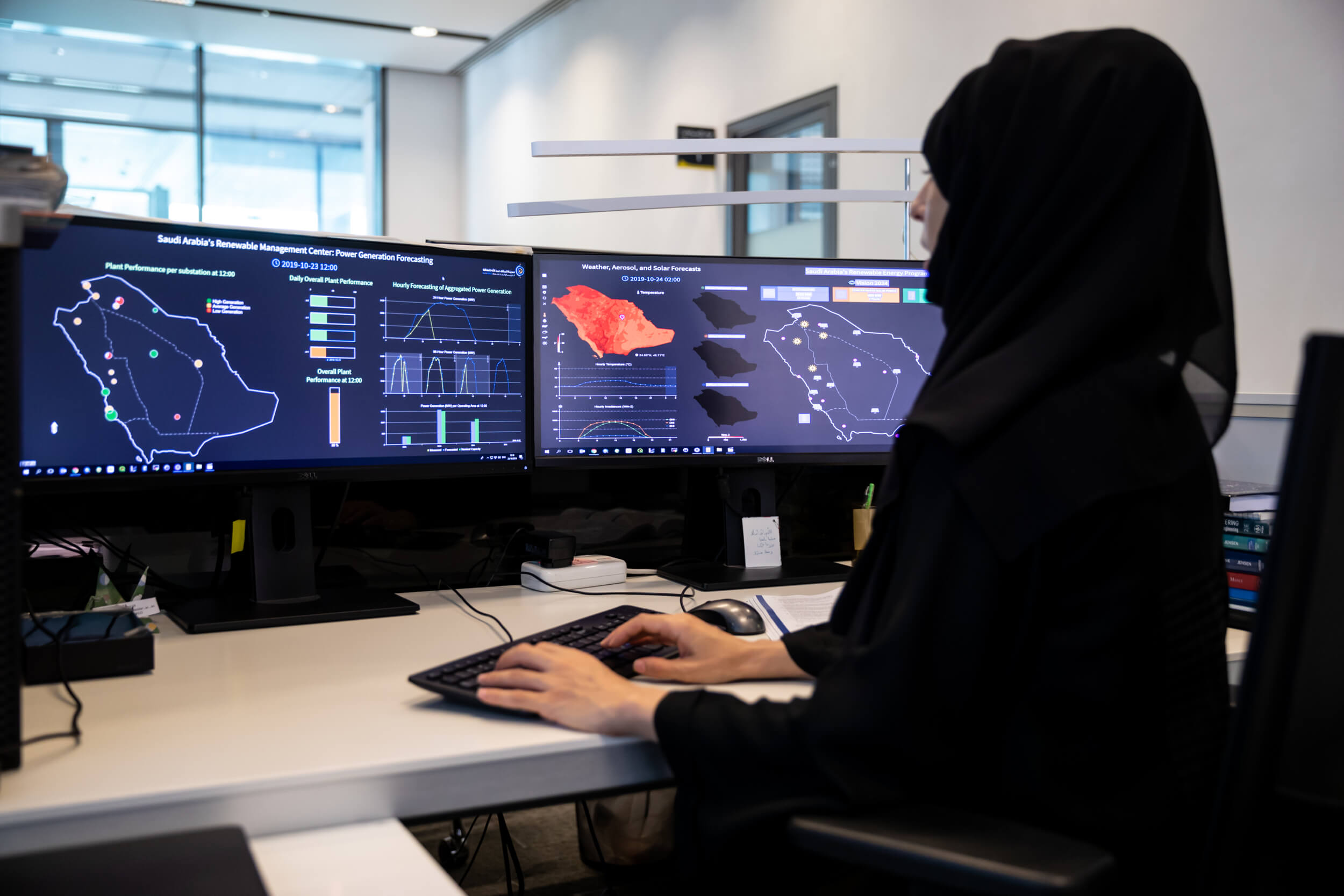
The Masdar Institute and Huawei, a leading global Information and Communications Technology (ICT) solutions provider, today announced that they have signed an agreement to jointly develop solutions to support public health in cities using Huawei’s internet-of-things (IoT) platform and Masdar Institute applications.
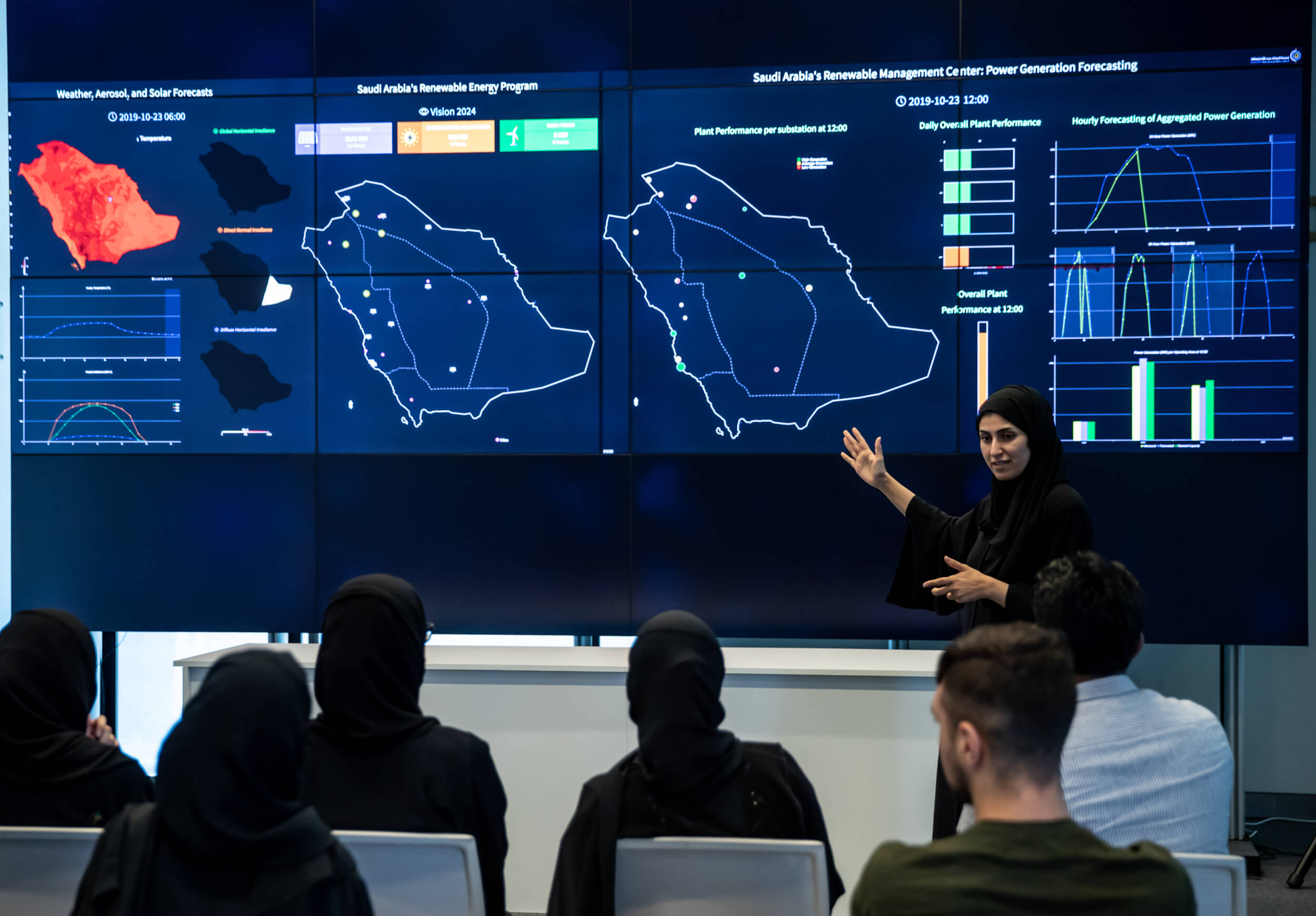
The project ultimately aims to provide real-time prediction and warnings for a variety of health risks for all city occupants, thereby improving their overall health. The applications are to be built on Huawei’s IoT Platform, which orchestrates data from multiple types of sensors. The data will come from commercial wearable sensors in the Masdar Institute campus that measure participants’ occupancy patterns and health data, like vital signs and body temperature, as well as wireless sensors that measure environmental data like humidity. The IoT solutions developed through this project will also play a critical role in transforming Masdar City, of which Masdar Institute is an anchor tenant, into a “smarter” and even more connected city.
Masdar Institute researchers will develop applications that can visualize the collected data and accurately predict a variety of health risks and provide recommendations for more healthy activities, based on environmental conditions and an individual participant’s physical health and location.
The two-year agreement was signed by David Wang, CEO of Huawei UAE, and Dr. Behjat Al Yousuf, Interim Provost, Masdar Institute. The agreement was signed at the Masdar Institute stand at the World Future Energy Summit (WFES) 2017, which is being organized as part of the Abu Dhabi Sustainability Week (ADSW) 2017 at the Abu Dhabi National Exhibition Center (ADNEC).
Dr. Al Yousuf of Masdar Institute said: “Environmental conditions, such as heat and dust, can increase the risk of medical conditions like respiratory disease. That is why leveraging advances in data analytics and IoT systems to aggregate, correlate and analyze this data to improve public health, seems an obvious and prudent solution to improve health and productivity. We are pleased to partner with one of the most innovative technology companies, Huawei, to achieve the important goals of improving our campus residents’ health and happiness, while also advancing health information systems for improved health for all people.”
The IoT platform provided by Huawei is well-suited for this project, as it provides a private cloud computing solution capable of dealing with large data streams, as well as device management capabilities.
“We are speeding into a future where billions of devices are going to communicate with each other, with people and organizations, so an open ICT architecture is fundamental to cope with the enormous amounts of data being generated,” said David Wang. “By deploying an open IoT ecosystem, Masdar City will be able to accelerate its digital transformation and take full advantage of IoT innovation by deploying smart city applications that can continue to support population growth and society as a whole.”
IoT systems are at the heart of a truly smart city. The IoT aims to transform data from sources that range from household appliances to business products to virtually anything in our surroundings, into value-added insights and intelligence for businesses and consumers.
Through the complete end-to-end IoT solution being developed for the Masdar Institute campus, the data collected on human health, occupancy patterns and environmental conditions will be converted into actionable insights that will ultimately empower Masdar City occupants to make better health decisions, leading to increased health, productivity and sustainability.
Associate Professor Dr. Mihai Sanduleanu and Assistant Professor Dr. Andreas Henschel, both from the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department, will be leading the project from Masdar Institute’s side.
“The main application is supposed to provide a real-time visualization and warning system capable of calculating probabilities for the health risks of all individual participants. A second application involves providing this data to health care providers and health authorities so that they may gain new insights about the interplay of health and environmental factors,” explained Dr. Sanduleanu.
In the second phase of the research project, the research team will employ Masdar Institute’s proprietary sensors to quantify human outdoor movements within Masdar City and correlate it with environmental data and city design. This data will help optimize human outdoor comfort.
Erica Solomon
News and Features Writer
18 January 2017